Advanced Tips for pH Neutralization Systems: Strategies, Techniques, and Compliance Insights
pH neutralization systems are processes and setups designed to adjust the acidity or alkalinity of liquids so they fall within an acceptable pH range. The pH scale measures how acidic or basic a solution is, typically from 0 to 14, with 7 considered neutral. Many industrial, municipal, and laboratory activities generate wastewater or process fluids that are either too acidic or too alkaline. pH neutralization exists to correct this imbalance before the liquid is reused, discharged, or treated further.
The concept of pH neutralization has existed for decades, closely linked to chemistry fundamentals and environmental protection needs. When untreated acidic or alkaline liquids enter natural water bodies, drainage systems, or downstream equipment, they can cause corrosion, environmental harm, and safety risks. Neutralization systems help prevent these outcomes by carefully adding neutralizing agents and controlling reactions.
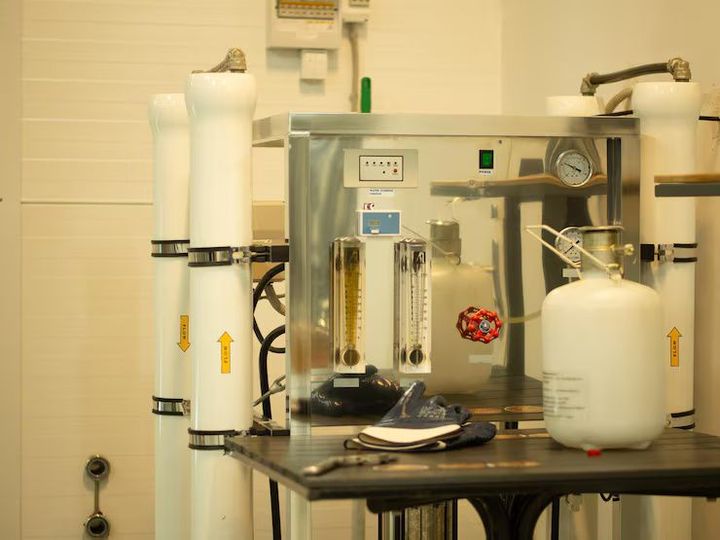
At a basic level, pH neutralization systems work by combining acidic and alkaline substances in controlled conditions until the desired pH is reached. Modern systems build on this principle with automation, sensors, and process controls that ensure accuracy and repeatability. This makes pH neutralization a foundational element in water treatment, chemical processing, and environmental management.
Why pH Neutralization Systems Matter Today
The importance of pH neutralization systems has grown as environmental awareness, industrial activity, and regulatory oversight have increased. Many sectors now rely on accurate pH control to protect ecosystems, infrastructure, and human health.
Key reasons pH neutralization systems matter today include:
-
Environmental protection: Preventing harmful discharges into soil and water bodies.
-
Regulatory compliance: Meeting discharge and treatment standards set by authorities.
-
Equipment protection: Reducing corrosion and scaling in pipes and machinery.
-
Process stability: Ensuring downstream treatment or processing steps function correctly.
-
Workplace safety: Minimizing risks associated with handling highly acidic or alkaline liquids.
Industries such as manufacturing, food processing, pharmaceuticals, power generation, and wastewater treatment are directly affected by pH control requirements. Municipal water authorities and laboratories also depend on neutralization processes to maintain safe and predictable conditions.
pH neutralization systems solve problems related to uncontrolled chemical reactions, environmental damage, and system inefficiencies. By stabilizing pH levels, they support safer operations and long-term sustainability across multiple sectors.
Core Strategies and Techniques in pH Neutralization
Advanced pH neutralization systems use a combination of chemical, mechanical, and control strategies to achieve reliable results. While the basic goal remains the same, modern techniques focus on precision, efficiency, and adaptability.
Common neutralization strategies include:
-
Chemical dosing: Adding acids or bases to adjust pH.
-
Batch neutralization: Treating a fixed volume of liquid at one time.
-
Continuous neutralization: Adjusting pH in a flowing stream.
-
Multi-stage neutralization: Using several reaction steps for better control.
-
Blending: Mixing acidic and alkaline streams to balance pH naturally.
The choice of technique depends on factors such as flow rate, pH variability, and required accuracy. The table below summarizes typical approaches:
| Technique | Key Feature | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Batch systems | High control | Variable waste streams |
| Continuous systems | Steady operation | Constant flow processes |
| Multi-stage setups | Fine adjustment | Tight pH limits |
| Blending methods | Reduced chemical use | Mixed effluents |
Advanced systems often incorporate real-time pH sensors and automated dosing controls. These components allow the system to respond quickly to changes in influent conditions, reducing overshoot and chemical waste.
Recent Updates and Industry Trends
Over the past year, pH neutralization technology has continued to evolve alongside broader trends in water treatment and industrial automation. During 2024, increased attention was given to digital monitoring, efficiency optimization, and sustainability.
Notable trends observed in 2024–2025 include:
-
Greater use of inline pH sensors with improved accuracy and durability.
-
Integration of automated control systems using programmable logic controllers.
-
Focus on chemical usage optimization to reduce excess dosing.
-
Adoption of data logging and analytics for compliance tracking.
The table below highlights recent focus areas:
| Trend Area | Focus | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Sensor technology | Faster response | Improved accuracy |
| Automation | Smart dosing | Stable pH control |
| Data systems | Continuous records | Easier reporting |
| Sustainability | Reduced chemicals | Lower environmental impact |
These updates aim to make pH neutralization systems more reliable, easier to monitor, and better aligned with modern compliance and environmental expectations.
Laws, Policies, and Regulatory Influence
pH neutralization systems are closely influenced by environmental laws and water quality regulations. Most countries establish acceptable pH ranges for wastewater discharge, surface water release, and industrial effluents. These limits are designed to protect ecosystems, infrastructure, and public health.
Regulatory considerations commonly include:
-
Discharge standards: Specifying allowable pH ranges.
-
Environmental protection laws: Addressing water and soil quality.
-
Industrial permits: Requiring documented pH control measures.
-
Monitoring and reporting rules: Mandating record-keeping and audits.
In many regions, updates introduced during 2024 reinforced the importance of continuous monitoring and accurate reporting. Government programs related to water conservation and pollution control indirectly support improved pH neutralization practices by encouraging efficient treatment systems.
Compliance with these frameworks requires reliable pH adjustment and documentation, making neutralization systems an essential part of regulated operations.
Tools and Resources for pH Neutralization Understanding
A variety of tools and resources support the design, operation, and evaluation of pH neutralization systems. These tools are primarily educational and analytical, helping users understand system behavior rather than promoting commercial activity.
Useful tools and resources include:
-
pH calculation tools for estimating neutralization requirements.
-
Chemical reaction simulators for modeling acid-base interactions.
-
Process flow diagrams illustrating system layouts.
-
Technical guidelines and standards documents related to water treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main goal of a pH neutralization system?
The main goal is to adjust liquid pH levels so they fall within an acceptable and safe range.
Why is pH control important before discharge?
Incorrect pH can harm ecosystems, damage infrastructure, and violate regulatory limits.
What substances are used for pH neutralization?
Acids or bases are used, depending on whether the liquid is too alkaline or too acidic.
How do automated systems improve pH neutralization?
Automation allows real-time adjustments, reducing errors and improving consistency.
Can pH neutralization handle fluctuating conditions?
Advanced systems are designed to respond quickly to changing flow rates and pH levels.
Conclusion
pH neutralization systems are essential tools for managing the acidity and alkalinity of liquids across many industries and environmental applications. Their purpose is rooted in basic chemistry, but modern systems apply advanced strategies, automation, and monitoring to achieve reliable and compliant results.
Recent trends emphasize efficiency, data-driven control, and sustainability, while laws and policies continue to shape how pH neutralization is implemented and documented. By understanding the context, importance, techniques, updates, and available resources, readers can gain a clear and practical view of how pH neutralization systems support safe operations and environmental responsibility.